HPA controller 源码解读
本篇讲述
kubernetes的横向 pod 伸缩(HorizontalPodAutoscaler) 控制器的数据结构,逻辑处理,metrics 计算以及相关细节的源码解读。
1. 前言
在 k8s 环境内弹性伸缩并不是一个陌生的概念,是一个常见且不难理解的事件。就是根据特定的事件或数据来触发可伸缩资源的伸缩能力。一般有 HPA 和 VPA 两个概念,HPA 全称 Horizontal Pod Autoscaler 即横向 pod 的自动伸缩,VPA 全称 Vertical Pod Autoscaler 即纵向 pod 的自动伸缩。
1.1. HPA
HPA 关注 pod 的数量,根据现有 pod 的数据(cpu, memory)或外部数据(metrics)来计算实际需要的 pod 数量,从而调整 pod 的总数。HPA 操作的对象需要实现 ScaleInterface 。
|
|
k8s 原生资源中 HPA 可操作性的对象是以下三个:
DeploymentReplicaSetStatefulSet
一般业务场景用 HPA 能满足需求,即业务高峰增加 pod 数更好处理业务,业务低峰降低pod 数节省资源。
1.2. VPA
VPA 关注的是 pod 的资源,根据当前资源利用率等数据为 pod 提供更多的资源(cpu,memory 等)。本人对 VPA 也是表面理解,所以这里不做详细的解读。
VPA 更适合大计算、离线计算、机器学习等场景,需要大量的 CPU,GPU,内存来进行计算。
2. 基础用法
通过以下命令开启对某个资源的 HPA 能力:
|
|
metric server 才能读取到cpu 利用率,默认是不开启的。详情请看官方文档: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server实际使用如下:
|
|
然后可以通过 describe 命令查看创建后 HPA 的详情:
|
|
可以从上述详情看到 HPA 资源的详细信息以及最下面的步骤信息,当进行伸缩时会同步伸缩过程和原因到 Events 字段上。
之后可以通过压测的方式将 cpu 的利用率提升然后可以到 Deployment 的 replicas 数量的提升,并压测结束一段时间(会有冷却时间)后又降到 1 个 replicas.
3. 数据结构
HPA 资源 YAML 结构:
|
|
上面对 HPA 的概念和如何使用有了一定的认知,从这里开始对 HPA Controller 的源码进行解读。
数据结构:
|
|
4. 控制器逻辑
4.1. 伸缩过程
伸缩过程的触发不是实时的,而是从 queue 里消费数据,进行一次伸缩流程,再次将资源名放入 queue, 完成一次循环。
详细流程如下:
4.1.1. 从 queue 读取一条消息,根据消息中的信息,获取 hpa 对象
|
|
4.1.2. 为了兼容老版本,读取时 hpa 对象为 v1 版本,读取后在代码里会先统一转换为 v2 版本,从而之后的逻辑统一
|
|
4.1.3. 根据 hpa.Spec.ScaleTargetRef 信息读到需要伸缩的资源
|
|
4.1.4. 确定当前副本数,最大最小可伸缩的副本数
|
|
4.1.5. 计算并处理副本数
|
|
4.1.6. 调整副本数
|
|
至此,伸缩的大流程是完成了,剩下的就是对细节的了解了。比如如何计算目标副本数的,如何处理伸缩的策略等等。
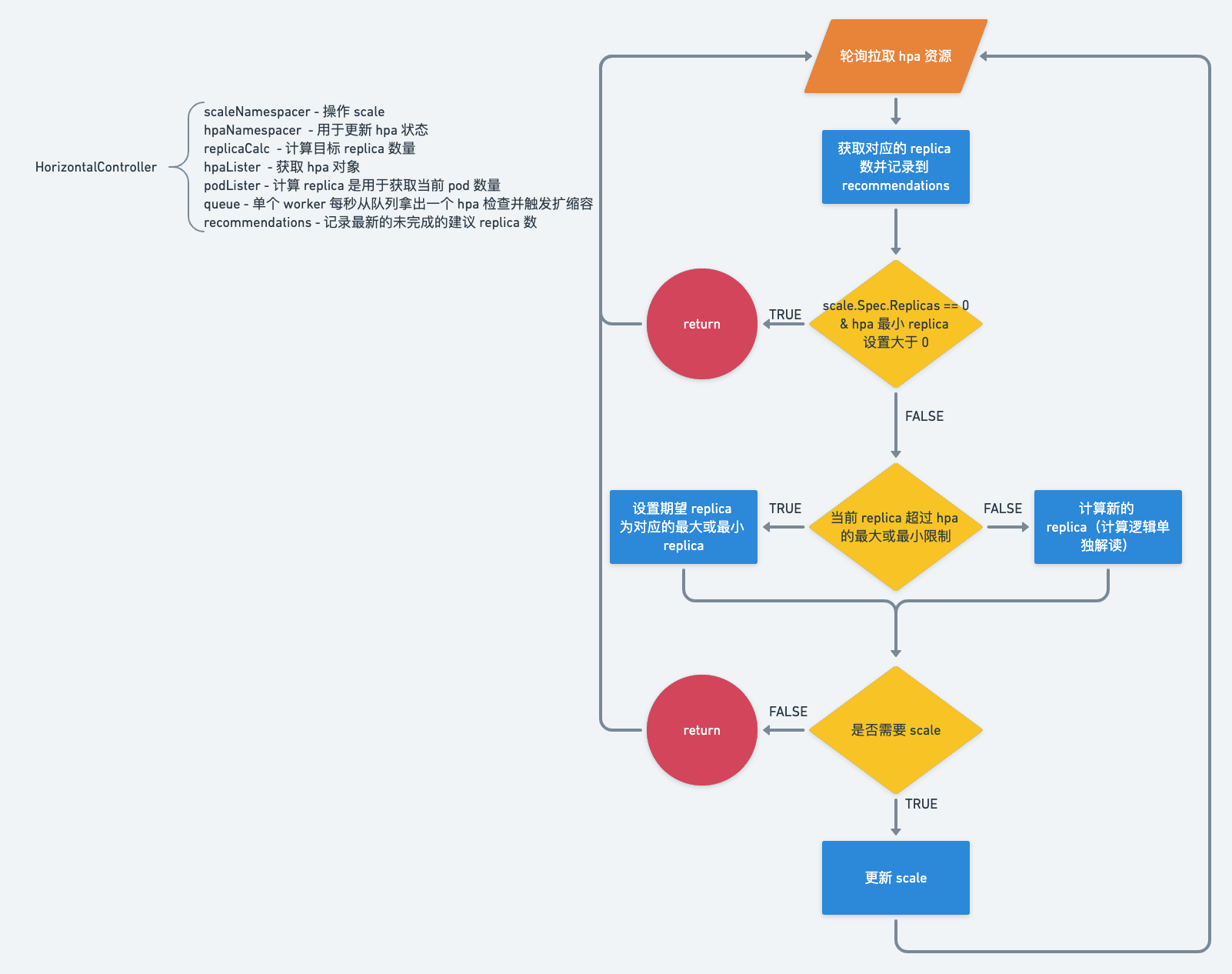
4.2. 计算副本数过程
可通过上面流程看到会有一个计算目标副本数的过程 a.computeReplicasForMetrics,看似简单其实内部相当丰富的一个过程,下面一起看一下如何去计算的。
4.2.1. 遍历 spec.Metrics 计算得出最大值
|
|
4.2.2. 计算单个 metric:根据类型计算 metric
hpa 对象的 spac.metrics 中的元素有个 Type 字段,记录 metric 数据源的类型,目前支持的以下几种:
| 类型 | 说明 | 支持的计算类型 | 不支持的计算类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object | 由 k8s 本身资源提供的数据,如 ingress 提供命中规则数量 | AverageValue Value |
AverageUtilization |
| Pods | 由 pod 提供的除 CPU 内存之外的数据 | AverageValue | AverageUtilization Value |
| Resource | pod 提供的系统资源(CPU 内存) | AverageUtilization AverageValue |
Value |
| External | 外部提供的监控指标 | AverageValue Value |
AverageUtilization |
-
AverageValue:设定平均值,如qps,tps。计算时读取 metric 总和,与预设平均值✖️副本数进行对比,从而判断是否需要伸缩。
-
Value:设定固定值,如队列中消息数量,Redis 中 list 长度等。计算时直接拿 metric 和预设值进行对比。
-
AverageUtilization: 平均利用率,如 CPU 和内存。先计算 pod的基数的总和(totalMetric 和 totalRequest),最终计算利用率 → totalMetric/totalRequest
源码:
|
|
下面会以 ExternalMetricSourceType 为例。
4.2.3. 根据计算类型执行对应的计算逻辑
下面以 External 的 AverageValue 为例
|
|
计算结果一路返回到
reconcileAutoscaler方法进行最终伸缩。
5. 扩展用法
在实际开发环境只用 cpu, memory 来作为弹性伸缩依据是远远不够的。大多数情况可能会根据 qps, tps, 平均延迟时间, MQ 中的消息数量, Redis 中的数据量 等与业务息息相关的数据量判断伸缩的依据,这些都属于 HPA 的 External 类型的范畴。但是 External 类型的数据源需要对接 Adapter 的方式才能用到 HPA 对象内容(具体请查看: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/horizontal-pod-autoscale/#support-for-metrics-apis) ,也就是说需要额外开发量的。
这里我推荐一个知名度比较高且支持的数据量比较广泛的 Adapter 的实现 – KEDA。基于事件驱动的autoscaler,且支持从 0 到 1 1 到 0 的伸缩,也就是说业务低峰或者无流量时可以降到 0 个副本数(这个在 HPA 被认为是禁用该功能 所以 KEDA 自己实现的 0 到 1 1 到 0 的伸缩的能力,剩余的情况它叫个 HPA 处理)。
目前 KEDA 支持事件类型如下:
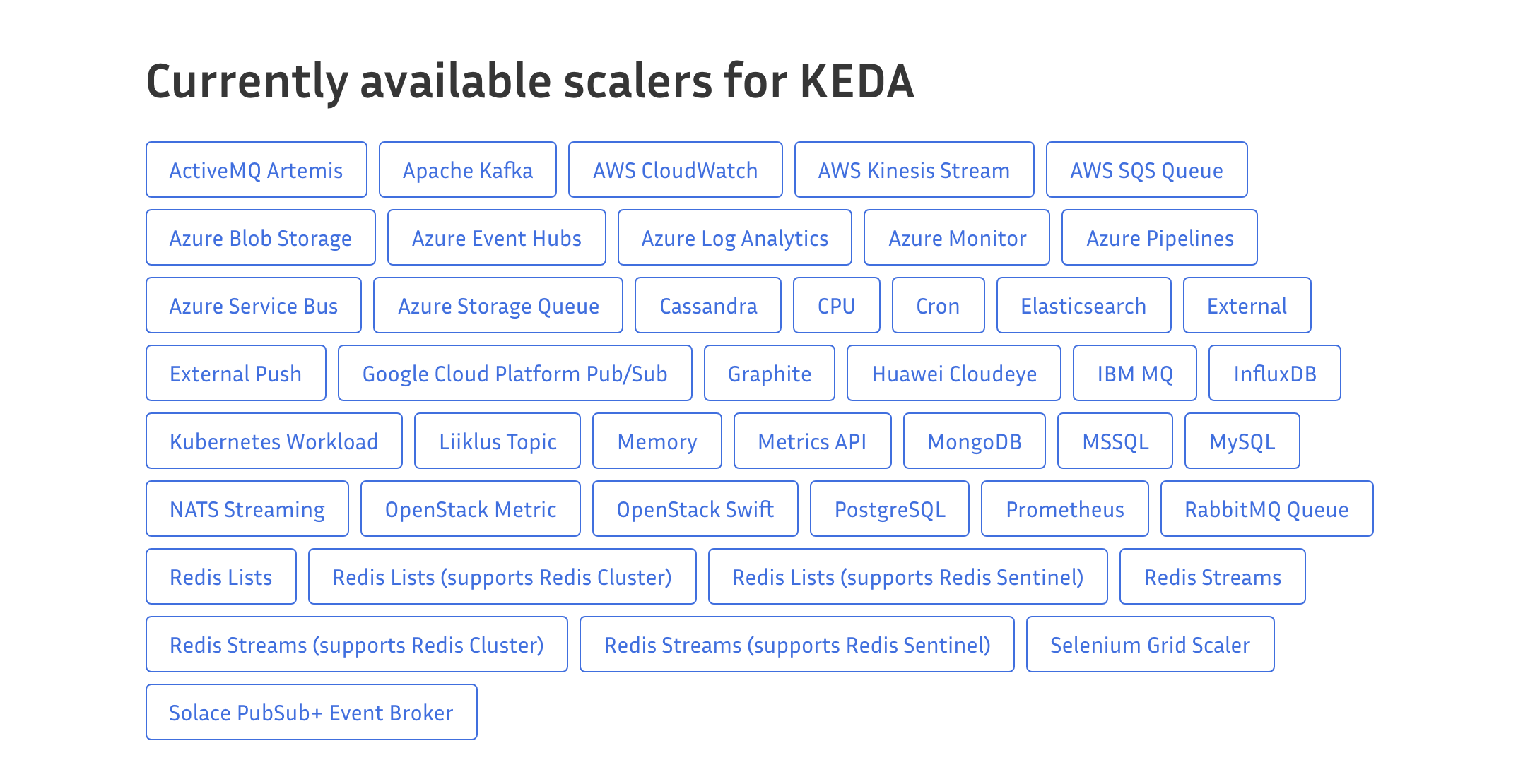
只需要创建 KEDA 的 CRD 资源,就能实现基于事件的弹性伸缩,KEDA 的 controller 会创建对应的 HPA 对象。
下面以 Prometheus 为例:
KEDA.ScaledObject:
|
|
apply 该 yaml 后,会创建一个 ScaledObject 和 HPA 对象。
|
|
这样一来,可以根据很多事件来控制伸缩的能力,这比单一来 cpu,内存利用率来看更灵活且及时。完全可以根据事件在服务的副本数不够用或者有一堆事件准备处理时,尽可能快速扩容,确保处理能力不会受损。
6. 总结
这篇文章主要讲 HPA controller 的源码和如何使用 HPA 相关内容
HPA/VPA的解释- 如何使用
HPA HPA Controller如何处理一次伸缩事件的HPA Controller如何计算目标实例数的- 认识和使用
KEDA– 一个基于事件驱动的 autoscaler
